Everything you need to know about scoliosis and treatment options
Scoliosis can impact people of all ages, from young children to adults, and its severity can vary widely. For some, the condition may cause minor symptoms, while others may notice significant changes in their posture or mobility. Detecting scoliosis early is important for successful management and finging the best posisble treatment options. By visiting a dedicated scoliosis clinic, you can access tailored care plans designed to meet your unique needs.

What a Scoliosis?

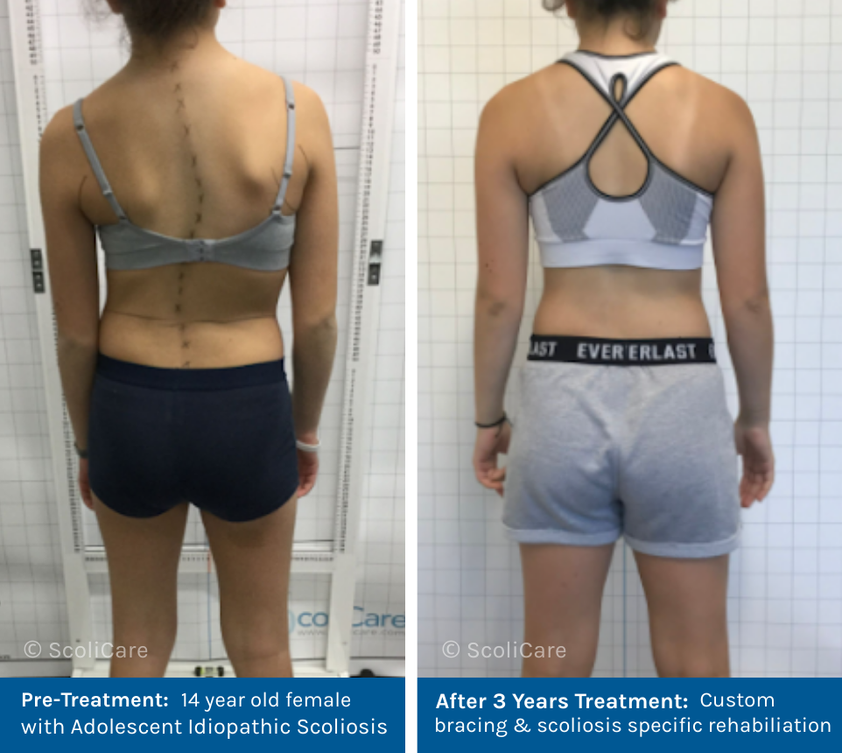
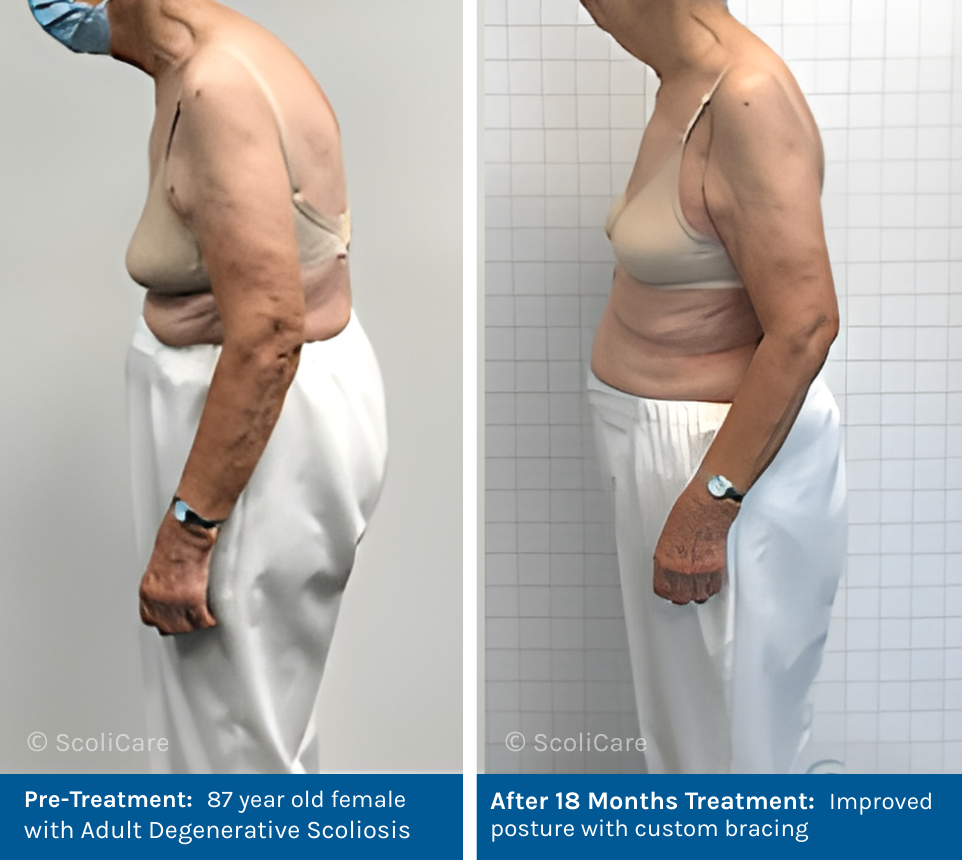
Scoliosis is often thought of as a condition that only affects teenagers. In fact, it can develop at any time. In adults, scoliosis can develop from a previously undiagnosed childhood condition or occur later in life due to degenerative changes in the spine. While some adults experience mild symptoms, others may see the curve worsen over time, potentially affecting mobility and quality of life. Early intervention with custom bracing and scoliosis specific rehabilitation can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is Infantile Scoliosis?

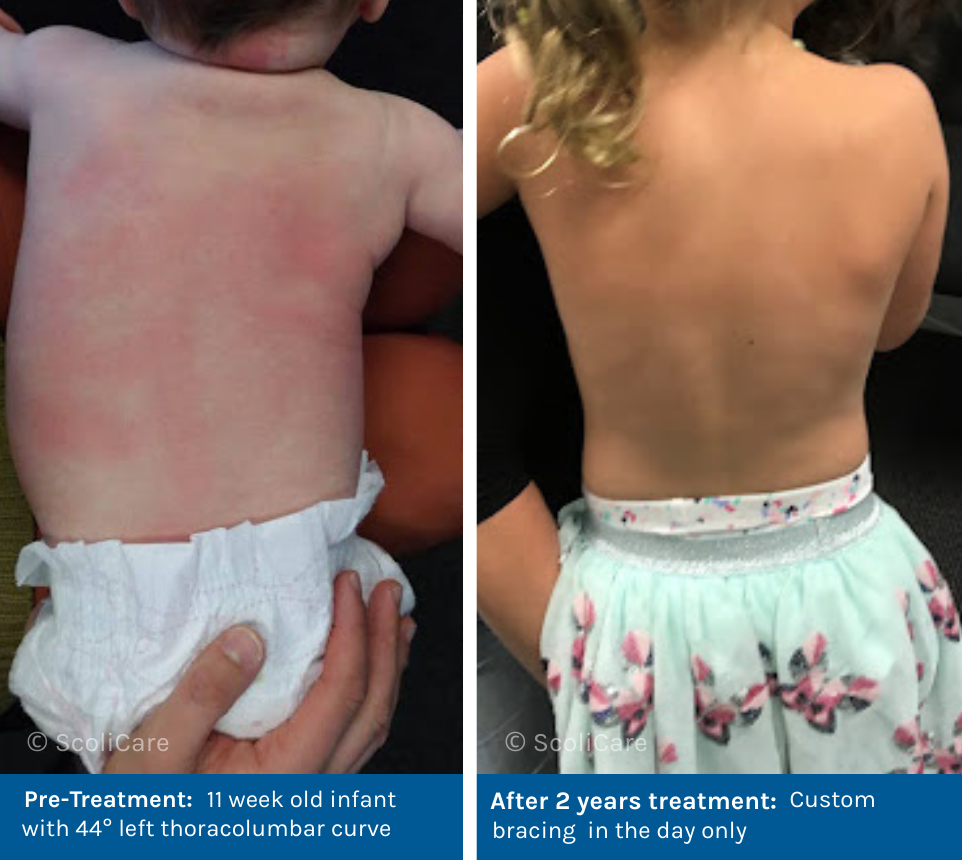
Infantile scoliosis occurs in children under the age of 4, usually presenting as a left-sided curve. While many cases may resolve naturally as the child grows, some can worsen over time, potentially leading to more serious problems. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing progression. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the curve and may include monitoring, casting, custom bracing, and in severe cases, surgery.
What is Adolescent Scoliosis?

What is Juvenile Scoliosis?

Juvenile scoliosis is a type of idiopathic scoliosis that affects children between the ages of 4 and 10 years of age. It is more common in girls, particularly between ages 6 and 10. The condition often worsens over time, with a higher risk of progression if not detected and treated early. In many cases, treatments such as custom bracing and scoliosis specific exercise rehabilitation are available as evidence-based treatment options for patients with Juvenile Scoliosis.
What is Infantile Scoliosis?

Infantile scoliosis occurs in children under the age of 4, usually presenting as a left-sided curve. While many cases may resolve naturally as the child grows, some can worsen over time, potentially leading to more serious problems. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing progression. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the curve and may include monitoring, casting, custom bracing, and in severe cases, surgery.
What is Scoliosis?

Scoliosis is a condition where the spine develops an abnormal sideways curve, often taking the shape of a “C” or an “S.” While the spine naturally curves when viewed from the side, it should appear straight from the back. Common signs can include uneven shoulders or hips, a visible spinal curve, leaning forward, hunching, or persistent back pain.
The condition can appear at any age – from infancy through adulthood- and its effects vary based on when it develops and how severe it becomes. Detecting scoliosis early makes a significant difference in treatment outcomes. That’s why regular check-ups and screenings are recommended at all stages of life to identify scoliosis promptly and begin appropriate management.
What is Scoliosis?

Scoliosis is a condition where the spine develops an abnormal sideways curve, often taking the shape of a “C” or an “S.” While the spine naturally curves when viewed from the side, it should appear straight from the back. Common signs can include uneven shoulders or hips, a visible spinal curve, leaning forward, hunching, or persistent back pain.
The condition can appear at any age – from infancy through adulthood- and its effects vary based on when it develops and how severe it becomes. Detecting scoliosis early makes a significant difference in treatment outcomes. That’s why regular check-ups and screenings are recommended at all stages of life to identify scoliosis promptly and begin appropriate management.
What is Scoliosis?

Scoliosis is a condition where the spine develops an abnormal sideways curve, often taking the shape of a “C” or an “S.” While the spine naturally curves when viewed from the side, it should appear straight from the back. Common signs can include uneven shoulders or hips, a visible spinal curve, leaning forward, hunching, or persistent back pain.
The condition can appear at any age – from infancy through adulthood- and its effects vary based on when it develops and how severe it becomes. Detecting scoliosis early makes a significant difference in treatment outcomes. That’s why regular check-ups and screenings are recommended at all stages of life to identify scoliosis promptly and begin appropriate management.
The benefits of non-surgical treatment
Scoliosis management can take many forms, with the most appropriate treatment depending on each individual’s needs. Non-surgical options – such as scoliosis-specific exercises and custom bracing – can help stabilise the spine, improve posture, ease discomfort, and promote long-term spinal health. These conservative approaches are often effective in slowing curve progression and improving day-to-day wellbeing. For more advanced or severe cases, surgery may be considered. The key is a personalised treatment plan, developed after a detailed evaluation by a dedicated scoliosis clinician, to ensure the most suitable path forward.

FAQ’s
Here are some commonly asked questions around Scoliosis and available treatments: